Google’s recent announcement reveals that the new Interaction to Next Paint (INP) metric will replace the First Input Delay (FID) as a Core Web Vital starting March 12th this year.
INP measures the time between a user’s interaction with a page (such as clicking a button) and the browser’s ability to display the corresponding changes on the screen. Its purpose is to consist of aspects of interactivity that were not covered by FID.
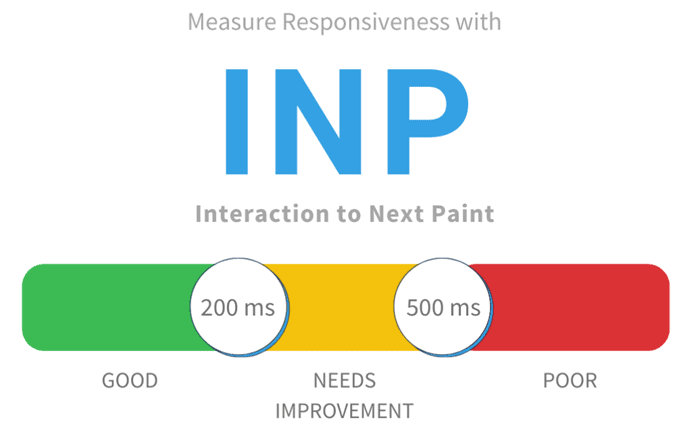
What is Google’s New Interaction to Next Paint?
Google’s Interaction to Next Paint (INP) is a metric introduced as part of Core Web Vitals, which measures the time between a user’s interaction with a web page (such as clicking a button or tapping on a link) and the moment when the browser renders the visual changes resulting from that interaction. Essentially, INP focuses on capturing the delay between user actions and the visual feedback displayed on the screen. This metric aims to provide insights into the responsiveness and interactivity of web pages, helping developers optimize their sites for a smoother user experience.
Advancing Web Metrics
In 2018, Google introduced First Input Delay (FID) as part of its Web Vitals initiative, aiming to measure the time to first paint following a user’s initial interaction. Web Vitals offers metrics to aid web developers in optimizing crucial facets of user experience.
As time progressed, Google identified the limitations of FID in evaluating interactivity, prompting the introduction of Interaction to Next Paint (INP) as an experimental metric in May 2022. Following a transition phase as a ‘pending metric,’ Google has affirmed that INP will formally replace FID in March.
Preparing for Transition
With the impending change to INP, developers are advised to ensure that their website’s INP aligns with the “good” threshold, indicative of performance at the 75th percentile of page loads.
For websites failing to meet this standard, Google recommends the following steps to optimize for the transition:
- Assess current INP performance using tools such as PageSpeed Insights and Chrome’s User Experience Report.
- Address problem areas by adhering to Google’s optimization guidelines. This might entail streamlining JavaScript code, minimizing input delay, simplifying DOM structures, or optimizing CSS selectors.
- Identify factors hindering INP, such as lengthy JavaScript tasks, excessive main thread activity, or a complex DOM.
Expanded Significance in Web Development
Google’s integration of INP as a Core Web Vital could have far-reaching implications for both web development and user experience:
- INP scores might influence website rankings on search engines and user engagement, given Google’s integration of Core Web Vitals into its ranking algorithm.
- There could be a requirement to update performance monitoring tools and strategies to effectively monitor and analyze the new INP metric.
- Web development methodologies may change towards prioritizing the optimization of interaction readiness, potentially needing adjustments to application architecture and code implementation.
As Google prepares to adopt the INP metric on March 12, web developers should assess their website’s performance and implement measures to enhance areas affecting interactivity.
Given the increasing importance of interactivity in search rankings and user engagement, developers should proactively prepare to ensure a seamless transition.
Would you like to read more about “Google’s New Interaction to Next Paint (INP) to Replace First Input Delay” related articles? If so, we invite you to take a look at our other tech topics before you leave!
Use our Internet marketing service to help you rank on the first page of SERP.
![]()