React Native is a framework created by Facebook that allows you to develop native mobile apps for iOS and Android with a single JavaScript codebase. React Native vs. Native.
In 2012 Mark Zuckerberg commented, “The biggest mistake we made as a company was betting too much on HTML5 as opposed to native”. React Native was announced at Facebook’s React.js conference in February 2015 and open-sourced in March 2015.
With the rise of React Native popularity and the growing number of popular mobile apps (such as Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, Uber, Discord, SoundCloud, Skype…) being partially or completely rewritten in React Native, the question arises: Should mobile developers use React Native for mobile development instead of going full native with Java or Swift?
React Native vs. Native
Before we start comparing these languages and frameworks, let‘s first see how React Native builds a mobile app. React Native framework uses React.js library to create a truly native mobile app. The important difference between React and React Native is that the latter uses native components instead of web components to create the user interface, along with JSX — a syntax that is used to embed XML with JavaScript.
This basically means that you can write mobile apps similar to how you would write web apps. Let’s show this on a simple custom component example:
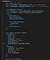
We can immediately see the similarities to the web development coding style. React Native components such as and are defined and organized exactly like HTML components such as
Also, styling React Native components with StyleSheet is almost the same as the good old CSS. The only difference is the field names are written in camelCase (borderRadius) instead of CSS dash style (border-radius).
React Native uses a set of components, which map to their native iOS and Android counterparts, and some platform-specific components, such as and iOS or Android.
Mobile App Development
Based on this, one could argue that it is definitely much easier, cheaper, and faster to write mobile apps in React Native instead of native iOS and Android. But is it really that simple? Let us discuss the pros and cons of each approach in more detail, based on specific criteria.
React Native enables a single JavaScript codebase for 2 different platforms. This means that it is easier to maintain the app by having the same development process for both platforms and reusing the same code. Still, it also requires fewer resources because there is no need for separate iOS and Android teams.
However, this benefit comes with a cost. It is well-known that Android and iOS have different design guidelines. Human Interface Guideline for iOS and Material Design for Android have a big share of differences, so if the project requirements dictate that these specific OS requirements should be followed for each native platform, React Native developers will need to write platform-specific code which defeats the purpose of the single codebase. This might be a bigger issue when it comes to iOS because Apple often updates and deprecates its technologies which can be hard to follow. At the same time, Android apps generally have more control of the system and are allowed more freedom.
However, if it is OK for the app to look the same on both iOS and Android, using React Native will greatly speed up the development and maintenance processes.
It should be noted, though, that even with the factor of being allowed to write an app that looks the same on both platforms, it is still impossible to write an app without writing any platform-specific code. Some components will look great on iOS and bad on Android and vice versa, which raises the need for fine-tuning those specific cases. Still, even with platform-specific UI in the code, having even 30% of the shared codebase is big money and time saved in the long run.
React Native is based on React.js, which is written in JavaScript. This is a major advantage when it comes to the fact that JavaScript is such extensive. And the popular language is that it’s tough to find a programmer who hasn’t used it at some point in their career.
What is the disadvantage of using JavaScript, though? Well… it’s JavaScript.
While Java and Swift/Objective-C are strongly typed, compiled languages, JavaScript is interpreted and often called an untyped language. This means that your variables can be anything at any time, and a compiler is not going to help you, so if you’re not extra careful while writing your apps, the floor is paved for Javascript horrors to ensue. When true native apps have more control of the variables and the app’s logic is more predictable, JavaScript relies on the programmer’s experience, Lint tools, and automatic tests. Does this mean that JavaScript programs have more errors by definition? No. But it does mean that you might spend a lot more time searching for that app-breaking error that your compiler would have gotten for you in Java or Swift.
Still, it is a fact that JavaScript remains one of the most widely-used programming languages in the world. And the maturity of the JavaScript community implies that finding a React Native developer for a project should typically be trivial.
Anyone who has ever worked in XCode or Eclipse / Android Studio knows how long and tedious the build time can be. This can especially be frustrating if you are working on a feature that is multiple screens away from the launch screen. This makes even trivial tasks such as changing a view color or changing a label text very time-consuming.
React Native’s solution for this problem is called hot reloading, which keeps the app running and saves the state (the data and the screen you’re on), only injecting the changes made in the code. While far from perfect, this feature works well for most of the usual use cases, saving a lot of precious development time.
React Native vs. Native
Even without using hot reloading, app build time is significantly faster using React Native than native iOS and Android. A live reloading mechanism can automatically reload the app every time the code is changed, having to build it manually every single time. React Native vs. Native
React Native’s approach to structuring UI is Flexbox, which is already very popular in web development. And enables the developer to create a responsive web or mobile UI very easily. It is a technology that rivals Android’s XML / Constraint layout approach or iOS’s Storyboard / XIB / Coding with UI libraries such as the Neon approach.
One considerable advantage that native mobile has. Though, is that you have access to all the native APIs such as Camera, Touch ID, and GPS and tools for creating animations and complex user interfaces. There is no middle layer, and you are free to take advantage of everything the mobile platform has to offer. Unfortunately, React Native does not excel at creating complex UI and animations. It has the Animated API, a neat solution but is still far behind the native capabilities.
React by default re-renders a component every time its state changes. If used well, this paradigm for building UI is superior. However, if not handled well, this can be a source of wasteful re-renders. Worth noting is that performance problems might arise in a single-threaded JavaScript environment. And you need to be extra careful while building your UI. React Native vs. Native
React Native vs Native (iOS, Android)
Also, some complex mobile features are best done in native. One example of this is Apple’s ARKit for creating augmented reality experiences. Another example is apps that are very platform-specific, such as apps for watchOS or tvOS.
React Native does not provide the amount of user interface power as native mobile does. So for apps that require a highly complex UI or sophisticated animations, it might not be the best choice. But for simple-looking apps, it is a better option because of the way Flexbox handles responsive UI layout and simplicity. And intuitive structuring of the XML components.
While React Native can handle many cross-platform use cases, it can’t cover all the native mobile ground. This means that there will always be a need for native modules. Native modules are basically coded in the native language, which handles a specific native feature. Examples of native modules are modules for the camera, native image picker, push notifications, deep linking, and third-party services like Auth0 or Amplitude.
These modules must be linked with the react-native link command, but in most cases, this will not be enough. And the developer will need to follow specific instructions to link the native module to work on both iOS and Android. React Native vs. Native
React Native vs Native (iOS, Android)
So, this means that basically any native code can be written in the native language if React Native cannot handle it. It also means that React Native developer is forced to dig in native IDEs (XCode / Android Studio) to enable the modules. An experienced native mobile developer will usually quickly find a way to link the library. But someone who is purely a React Native developer and has never made a truly native mobile app will hit many walls before finally connecting everything. React Native vs. Native
In addition, it is worth noting that if the team uses a cloud service for Continuous Integration such as Azure. Even more, native linking problems might arise. Because XCode and Android Studio on the cloud might have a different version and configuration than your local one. So even if everything works well on your machine, it might not build remotely. The developer will need to do more fine-tuning for the linking to work on both sides.
The same goes for publishing the app. If the team doesn’t have developers experienced in native iOS and Android, they may struggle to release the app. This is more of an iOS problem, with the Android release workflow being more straightforward. To release an iOS app, React Native developers will still need to use XCode to configure release-related data such as provisioning profiles and certificates, which can be overwhelming at first.
React Native
All of this leads to a significant conclusion: React Native is much more effective if used by developers who already have experience with native mobile development. Because it doesn’t completely remove the need to go native.
While native iOS and Android are here to stay. And they will remain with us in the foreseeable future, the future of React Native is uncertain. React Native community is growing and expanding very quickly, but the current React Native version still not being 1.0 (the most recent version at the time of writing this article is 0.56). We are yet to see the best from React Native.
Facebook develops it, so the React Native developers are at its mercy. Because it is possible that at some point, Facebook decides to stop maintaining it. This has happened before with Facebook’s backend as a service platform called Parse, which shut down on 28 January 2017, forcing all current users to switch to a new service. The thought of this happening to React Native is scary indeed, but it could happen.
Also, React Native tends to keep up with the native trends. There will always be a time gap between some new feature (Face ID, for example) emerging on the native platform. And the same feature is included in React Native. This means that developing anything using fresh technology will take more time.
Another thing worth noting is that Facebook regularly updates React Native. But they are not very interested in fixing bugs that don’t directly involve the Facebook app. The way react-native compiles XML to native code is a black box process. So, if there is some error in a React Native component. You will either have to wait for Facebook to fix it or fix it yourself, which requires going into native code.
In the end, is React native worth it? The answer is: It depends on your project.
- Do you need to make an iOS-only or Android-only app? Go native.
- Do you have a small team with limited time and resources and need to make an app for both platforms? Go React Native.
- Do you need to make a highly complex app that utilizes a large portion of platform-specific code? Go native.
- Do you want to take advantage of fast build time and features such as hot reloading and live reloading? Go React Native.
- Do you plan to maintain the app over a long period of time, without fear of Facebook quitting React Native? Go native.
- Do your developers have a strong React / Web development background? Go React Native.
- Does your app need to support new mobile OS features as soon as they are released? Go native.
- Is your app going to look and behave the same on both platforms? Go React Native.
The key thing about React Native is that it’s still in development, and we are yet to see its full potential. In the future, it may be more powerful and efficient and allow for even more use cases. But for now, it cannot fully replace native mobile development. However, its write once, use everywhere paradigm can be a tremendous time and money saver if used on the right projects. React Native vs. Native
Needless to say, I am very excited to see how React Native will evolve and how it will affect the mobile world!
Would you like to read more about React Native-related articles? If so, we invite you to take a look at our other tech topics before you leave!