During a recent video, Google’s John Mueller addressed the impact of semantic HTML on search engine understanding of website content. Mueller explained how semantic HTML influences various aspects, including SEO, accessibility, and search rankings.
Before diving into the details, it’s essential to establish a clear understanding of semantic HTML and its functioning.
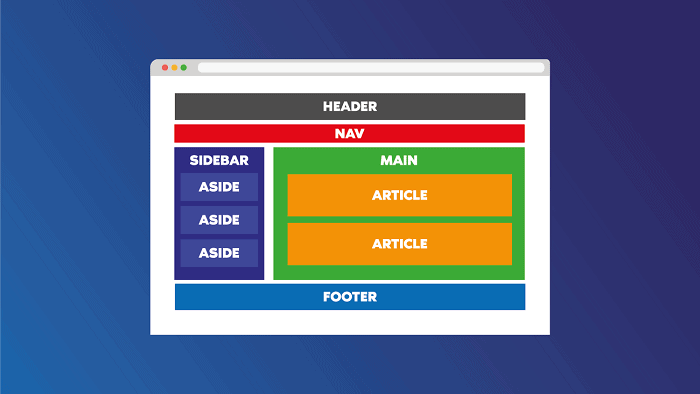
What is Semantic HTML
Semantic HTML refers to the practice of using HTML elements that convey meaning and structure to both browsers and developers. It involves choosing appropriate HTML tags that accurately describe the content they enclose.
Semantic HTML goes beyond the basic formatting and presentation of web pages. It focuses on providing context and understanding to both human users and search engines. By using semantic HTML, you can create well-structured web documents that are more accessible, maintainable, and search engine-friendly.
For example, instead of using a generic <div> tag to define a section of your webpage, you can use semantic tags like <header>, <nav>, <article>, <section>, <footer>, and <aside>. These elements not only organize the content visually but also provide meaningful information about the purpose and role of each section.
By utilizing semantic HTML, you enhance the clarity, accessibility, and search engine optimization (SEO) of your website, as it helps search engines understand the content and context of your web pages more effectively.
Semantic HTML elements play a crucial role in providing meaning and structure to web content.
By using these elements, you enable search engines and browsers to gain a deeper understanding of the content and the relationships between different elements on the page. This enhanced understanding facilitates improved indexing, accessibility, and overall user experience.
You may also like: In-Depth Website Development Guide For Beginners
Some common semantic elements include the following:
Headings are essential for denoting the importance and establishing a hierarchical structure within web content. The <h1> tag signifies the highest level of importance, while <h6> represents the lowest level.
Paragraphs, represented by the <p> element, are used to present blocks of text, allowing for better organization and readability.
Lists play a crucial role in organizing items. The <ul> tag creates unordered lists, while the <ol> tag creates ordered lists. Each item within a list is defined by the <li> tag.
Tables, created using the <table> tag, are used to structure tabular data. Rows are defined by the <tr> tag, column headers by the <th> tag, and data cells by the <td> tag.
Links or anchors, represented by the <a> tag, enable the creation of hyperlinks between pages, establishing connections and facilitating navigation.
Images, represented by the <img> tag, are used to display photos or graphics. The alt attribute provides a text description of the image, contributing to accessibility and SEO.
Articles, denoted by the <article> tag, represent independent and reusable content, such as blog posts or news stories.
Sections, indicated by the <section> tag, group related content together, often representing chapters or distinct parts of a document.
Asides, represented by the <aside> tag, contain content that is tangentially related to the main content, such as sidebars or supplemental information.
Figures, created using the <figure> and <figcaption> tags, represent images, diagrams, or illustrations accompanied by a caption. They help establish the relationship between the media and the surrounding text.
Is Semantic HTML A Ranking Factor?
According to Mueller, although semantic HTML does not directly impact search engine rankings, it plays a significant role in improving SEO and accessibility. It is considered a fundamental best practice in web development.
While semantic HTML may not provide an immediate boost to rankings, its use enhances the overall optimization for search engines. Moreover, by adhering to semantic HTML practices, you can create a website that offers an optimal user experience, aligning with the core principles of search engine optimization.
You may also like: Importance of Meta Tags in SEO: Explained
How Semantic HTML Benefits Google
Properly utilizing semantic HTML elements can contribute to SEO in the following ways:
- Structuring Text with Headings: Using heading tags (such as h1, h2, etc.) helps organize and structure passages of text, making it easier for search engines to understand the content hierarchy.
- Associating Images with Relevant Words: Placing images next to relevant textual content and utilizing alt attributes appropriately helps search engines establish the context and relevance of the images within the page’s content.
- Using Table Tags for Data Tables: Employing table tags (table, tr, th, td) specifically for organizing tabular data improves the accessibility and comprehensibility of the content for both users and search engines.
- Prioritizing Anchor Links over JavaScript-based Links: Employing anchor links (<a> tags) instead of relying solely on JavaScript-based links ensures that search engines can easily crawl and index the linked pages.
Mueller emphasizes that Google’s algorithms are not overly concerned with the specific choice of similar elements. While section, article, and div elements may be treated similarly, the essential aspect is to maintain a clear structure and establish relationships between elements. Ensuring a logical and coherent structure is more significant than the specific HTML element used.
You may also like: What Is A Sitemap: Explained
How Semantic HTML Benefits People
Semantic HTML significantly enhances the user experience for individuals with diverse backgrounds and disabilities. It achieves this through the following means:
- Assisting Screen Readers: By employing semantic HTML, screen reader software can effectively interpret and convey web content to blind or visually impaired users, enabling them to access and navigate websites with greater ease.
- Ensuring Keyboard Navigability: Semantic HTML elements, such as `<a>` links and `<input>`/`<button>` forms, can be easily accessed using keyboard controls, benefiting users with motor impairments who rely on keyboard navigation.
- Supporting Assistive Technologies: Assistive technologies like Braille readers and text-to-speech software benefit from the clear structure and meaning provided by semantic HTML, enabling a more effective translation of content for users with disabilities.
- Facilitating Responsive Web Design: Semantic HTML aids in the creation of responsive web designs, ensuring that content remains accessible and adaptable across a range of devices, including mobile phones and tablets.
- Future-Proofing Content: By adhering to web standards through semantic HTML, developers can create content that is more likely to remain accessible as technology advances. This future-proofs the content, ensuring that all users can access it regardless of the devices or technologies they use.
By following the principles of semantic HTML, developers can create web content that is easily understood by both humans and machines, fostering a more inclusive and accessible web experience for all users. Hire an Internet marketing service London to help you rank on the first page of SERP.
Would you like to read more about the importance of semantic HTML in SEO-related articles? If so, we invite you to take a look at our other tech topics before you leave!








