Cyberattacks are not random occurrences but rather stem from unresolved risks. Any functioning network can be susceptible to threats. Rather than waiting for hackers to exploit vulnerabilities in your system, it is advisable to take a proactive approach by assessing both the inherent and residual risks.
By comprehending the inherent and residual risks present in your network, you can gain valuable insights into how to improve its security. What exactly are these risks, and what measures can you take to mitigate them?
What are Inherent Risks?
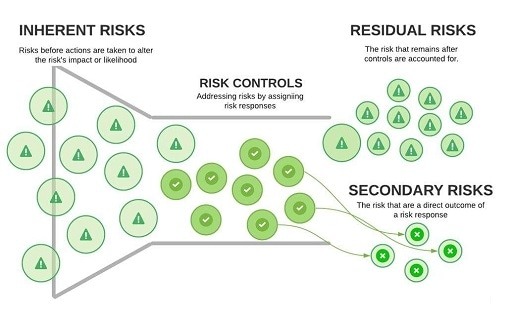
Inherent risks are those vulnerabilities and threats that may prevail in a system or organization where no security controls or measures are implemented. Inherent risks result from many factors, such as system design, type of software or hardware used, or even the nature of the business or operation.
Inherent risks could be identified through some forms of risk assessment: analyzing both the threats and the vulnerabilities that exist within either the system or the organization. Examples include weaknesses in software applications, access controls, or data backup and recovery procedures.
Controls can be put in place to mitigate the probability of an attack and the associated impact, but some vulnerabilities are intrinsic and cannot be completely removed; an organization should stay in a state of vigilance and keep reassessing its security posture to make sure that any emerging vulnerability is dealt with immediately.
Inherent Risks can be defined as the vulnerabilities existing in your network when there are no security policies, procedures, or protocols put in place that could deter these threats.
Of course, that would be too absolute because one cannot measure that which does not exist. It could be said more precisely that an inherent risk represents the vulnerabilities existing in your network when it operates at its default security settings.
Think, for instance, about doors in your house: should you not install locks on them, intruders can easily get inside because nothing will stop them. In the same vein, there are a number of vulnerabilities that are waiting in store in a network that is bereft of appropriate security measures.
What are Residual Risks?
Residual risks are the vulnerabilities in your system once you have implemented security measures, including procedures, processes, and policies, that protect your valuables.
Even though you have set up a defense mechanism to deter cyber threats and attacks, there is still some form of risks which could come up and affect your system.
Residual risks indicate that security is not a one-time thing. Locking your doors does not mean criminals cannot attack you. They may find means of opening the locks or breaking your doors down even if it calls for going extra miles to do that.
Residual risks are the ones that remain after the application of security controls or mitigating measures against an inherent risk.
These are there because of a number of factors, including but not limited to the inability of the security controls to completely eliminate the vulnerabilities, evolution of new threats that were not there in the first place, or even human error or negligence.
You can also read: 5 Reasons Cyber Security is Important for Everyone
Residual risks can be minimized through regular monitoring and assessment of the network’s security controls, with the addition of more controls or modification of existing controls to handle any new vulnerabilities that may arise.
It is important to note that residual risks cannot be entirely eliminated but can be reduced to an acceptable level through continuous risk management and security measures.
Inherent and Residual Risks in Cybersecurity
In summary, inherent risks refer to the potential risks that exist in your system when there are no security defenses in place, while residual risks are the risks that may persist even after implementing security measures. A comparison of the security implications of these risk categories can reveal further differences between them.
Effect of Inherent Risks
The common implications of inherent risks include:
Data Loss Due to Lack of Security
To ensure effective data protection, strong and intentional security controls are necessary. Relying on default security settings alone is insufficient in guarding against calculated cyberattacks.
Cybercriminals are constantly seeking potential targets, and inherent risks expose your assets to these attackers. The absence of robust security measures makes it easier for them to infiltrate your network and steal your data without encountering significant obstacles.
Non-Regulatory Compliance
There are several regulatory standards in place to safeguard user data. As a network owner or administrator, it is your responsibility to adhere to these regulations to ensure the security of your users’ data.
Failure to establish policies that guide compliance with regulatory requirements in your industry can expose your network to inherent risks. The lack of policies for user engagement may result in compliance violations, which can lead to sanctions, lawsuits, and penalties.
You can also read: 5G Security Risks you should know
Network Breach Due to a Lack of Access Control
At its core, protecting your data involves implementing access controls to monitor who has access to specific information. Inherent risks often stem from a lack of access controls on systems. Without proper management of access levels among users, anyone can potentially access and compromise your most sensitive data.
Effect of Residual Risks
Here are some common implications of inherent risks.
Malware Attacks
Having security measures put in place on your system does not shield you from cybercriminals who might use unsuspecting methods like phishing attacks that will lead you to perform some actions that will compromise your system with malware.
Malware usually carries viruses that can pass through your system’s security and allow the attacker access and control; this is a residual risk since it may happen even when strong defenses are in place.
Insider Threats
Not all cyber threats are external, as threats can emanate from users in your network. Despite the installation of security defenses, deliberate or accidental insider threats can occur and compromise your network.
Insider threats are a part of residual risks since they can bypass the existing security measures, especially when those measures have been focused on the external ones and have overlooked the internal ones.
Third-Party Applications
When you integrate third-party applications into your system, you are only creating new entry points that a potential attack could use to get past any defenses you may have up. These devices increase your attack surfaces, and because you have very limited control over them, there is very little you can actually do to secure them.
Threat actors would look at the open ports in your system to outline the easiest entry points through which they can cause harm, and intercept your communications without necessarily causing any disruptions through methods like a man-in-the-middle attack.
How to prevent Inherent and Residual Risks
Although inherent and residual risks may differ, both can pose significant threats to your network if left unaddressed.
To prevent these risks and ensure a more secure network, consider the following measures:
-
Classify Risks Into Categories
When it comes to risk assessment, risk classification is crucial in establishing both qualitative and quantitative metrics. In order to properly address inherent and residual risks, it is important to identify and categorize the attributes of each risk type.
For residual risks, it is important to implement security measures to protect the affected areas rather than leaving them unprotected. Mitigation strategies should also be established, such as an effective incident response plan to address any attacks that may bypass your defenses.
-
Conduct Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the process of identifying, evaluating, and quantifying the various risks that exist within your network and the potential impact they could have. This includes identifying your assets and assessing their level of exposure to cyber threats and attacks.
You can also read: How to Keep Your PC safe and Secure from Viruses and Cyber Attacks
Understanding your cyber risks enables you to develop effective strategies for risk prevention and implementing security measures tailored to address the specific risks identified in your assessment.
-
Standardize Risk Prevention Controls
Using standard security frameworks such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27001, and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is an effective way to address cyber risks. These frameworks have been tested and proven, and they provide a basis for measurement and automation.
In the case of inherent risks, these frameworks can provide a solid foundation for implementing security controls from scratch, given the absence of substantial security. For residual risks, the frameworks can be used to identify and address any loopholes or weaknesses in the existing security structure.
-
Create a Risk Register
To a large extent, cyber risks are inevitable, and how they impact your system depends on your actions. Your knowledge of past cyber incidents can enhance your ability to manage present and future risks.
If a risk register exists, look for the cyber incident history. If there is none, gather information from helpful sources to create one.
The risk register should contain details of previous cyber risks and the measures taken to resolve them. Effective measures can be implemented again, but ineffective ones should prompt you to seek new and improved defense strategies.
Avoid Inherent and Residual Risks with holistic Cybersecurity measures
Comprehensive security should be the foundation of your security infrastructure. By considering all aspects of your system in your security efforts, you can address both inherent and residual risks.
Integrating a strong cybersecurity culture with effective processes and technology will enable you to mitigate risks to the greatest extent possible.
Would you like to read more about “What is Inherent and Residual Risks in Cybersecurity-related articles”? If so, we invite you to take a look at our other tech topics before you leave!
![]()