PDF OCR: Barcodes are such universal technology that it is easy to take them for granted. For years, barcodes have been revolutionizing the way we do business in industries like retail, travel/hospitality, entertainment, science, and advertising.
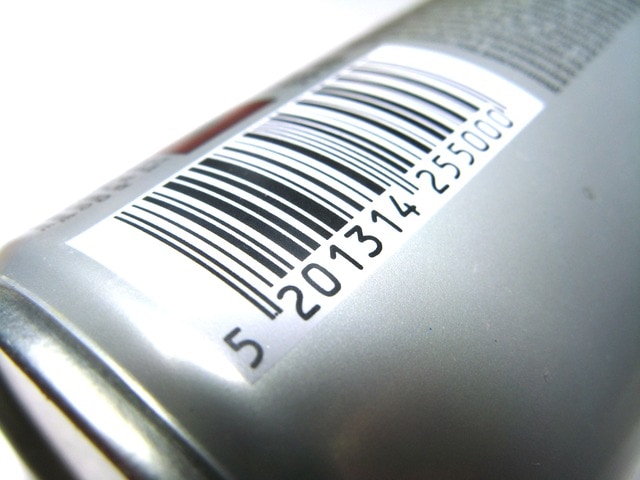

Today, barcodes are scanned 6 million times a day. They can serve many purposes, from tracking store inventory to enhancing marketing campaigns.
We answer the question: what is a barcode and how do you read one? Plus, we let you know how barcodes can work for you?
What Is a Barcode?
A barcode is basically a series of black lines and white spaces. A scanner reads them. Invented in 1952, barcodes are a means of tracking inventory. There are two kinds of barcodes: 1-dimensional and 2-dimensional.
1D Barcodes (pdf OCR)
Known as universal product codes or UPC, these codes are designed to store text information about products, including type, size, and color. They’re also used to track packages and for ISBN numbers on books. They’re read by a traditional linear barcode scanner.
2D Barcodes
This technology includes QR codes. They can include text as well as more complex information, including price, quantity, and even images. Smartphones or other image scanners read these types of barcodes.
You’ll find many variations of barcodes, all with different uses and applications.
Uses of Barcodes (pdf OCR)
Barcodes have many uses other than simply tracking inventory. Some of them may not have occurred to you, which means you might not be taking full advantage of the technology.
- Tracking store inventory
- Tracking packages & envelopes
- Passenger check-ins (planes, buses, trains, etc.)
- Registering & tracking store/club memberships
- Storing contact information & emails
- Marketing tool to promote products, services, sales, product launches & special events
- Direct customers to products in a store or restaurant menus
These are just a handful of the advantages of using barcodes.
How to Read a Barcode
So, how do barcodes work? How do you know what information a barcode can track? Reading them depends on the type of barcode. You might also like 10 Amazing Tips to Manage Your E-commerce Website
Reading UPC (12-digit) & UPCE (6-digit) codes:
- Used on standard labels and packages
- Product manufacturers receive a manufacturer’s ID code (GS1 US)
- Every barcode includes an ID number
- 7 lines define the code numbers, and each number follows a pre-established pattern
- The sum of the four numbers always adds up to 7
The UPCE 6-digit code has most of the same information, but it’s more condensed.
Reading 2D barcodes:
- 2D barcodes carry information vertically & horizontally
- Must be read by a smartphone or other reader devices
- QR codes have a “finder pattern” to detect the size, direction & angle of the square
- QR codes also have an alignment pattern to detect distortion
- Software analyzes the image, calculates the ratio between white/black areas & determines which parts contain data
Here is your source for pdf OCR c# for 2D barcodes.
The Universal Language of Barcodes
If you’ve ever asked yourself what is a barcode and can they benefit your business, this guide is a good start in understanding them. Make sure you learn more so you can find ways to increase efficiency, track inventory or packages, and market your products or services.
Be sure to check out our site to learn more about the latest computers, mobile devices, and other tech tools.
![]()