An Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) flood attack is a sort of denial-of-service (DoS) attack that involves flooding a target system with requests by using the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). It is also possible to use it to target individual workstations as well as servers.
It is essential to have a solid understanding of what an ICMP flood assault is and how it operates in order to successfully defend against one.
What is an ICMP Flood Attack and How Does It Work?
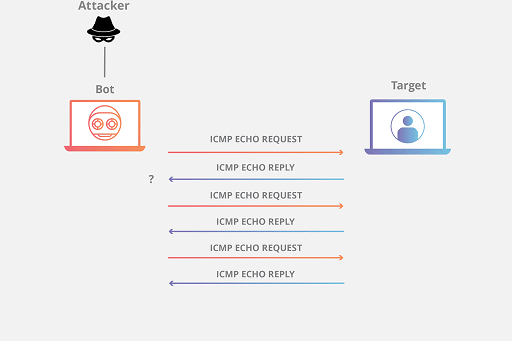
An ICMP flood attack, also known as a ping flood attack or a smurf attack, is a type of network layer DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack in which the attacker attempts to overpower a targeted device by sending an excessive amount of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets. Other names for this type of attack include a ping flood attack and a smurf attack. These packets are transmitted in fast succession in order to overwhelm the device that is the target of the attack, so preventing the device from processing traffic that is legal. As part of a multi-vector assault, this particular form of distributed denial of service attack is frequently combined with other DDoS assault methods.
Either a server or the network as a whole could be the target of the attack. The sheer volume of these requests can cause the target to become overwhelmed, which can lead to an inability to process legitimate traffic, disruption of services, or even complete system failure. These issues can arise because of the sheer volume of these requests.
The vast majority of ICMP flood attacks make use of a tactic known as “spoofing,” in which the attacker will send packets to the target with a spoofed source address, making it appear as though the packets are coming from a reliable source. This makes it more difficult for the target to distinguish between traffic that is legitimate and traffic that is malicious.
The attacker will use spoofing to send a large number of ICMP echo requests to the target. As each request is received, the target is forced to respond with an ICMP echo response because it has no other choice. This can quickly overwhelm the device that is the focus of the attack, causing it to become unresponsive or even crash.
Last but not least, the attacker might send ICMP to redirect packets to the target in an effort to further disrupt the target’s routing tables and render it incapable of communicating with other nodes on the network.
Techniques for identifying an ICMP Flood attack
There are a few telltale indications that can point to the possibility of an ICMP flood assault being launched.
-
An exceptionally high volume of traffic going outbound
An abnormally large amount of outgoing traffic from the device being attacked is another sign that it is being targeted by an ICMP flood assault. This is owing to the fact that the echo-response packets that are delivered back to the system that is being attacked are typically more numerous than the ICMP requests that were sent in the first place. It is possible that an attack is now taking place if you see that the amount of traffic on the device you are monitoring is significantly higher than usual.
-
An abrupt rise in the network traffic
A sudden surge in network traffic is the most typical sign that a computer is attempting to launch an ICMP flood attack. A high packet rate coming from a single source IP address is frequently observed in conjunction with this phenomenon. This is something that can be easily tracked using tools for monitoring networks.
-
Excessively high packet rates originating from one IP Address
The machine that is being used by the attacker will frequently transmit an abnormally high number of packets from a single source IP address. These can be found by monitoring the traffic that is coming into the device that is being targeted and looking for packets that contain a source IP address and an unusually high packet count for that address.
-
Increase in CPU usage of the target system
An ICMP flood attack may also be indicated by the target system’s level of CPU consumption if the attack is successful. The CPU of the target device is put under increased strain as more and more requests are sent its way in order for it to be able to handle them all. When this happens, there is a sudden rise in the amount of CPU time being used, which, if it is not addressed, can cause the system to become unresponsive or possibly crash entirely.
-
Unpredictable jumps in network latencies on a regular Basis
A potential indicator of an ICMP flood attack is a network that is experiencing latency. The amount of time it takes for new packets to arrive at their destination lengthens when the attacker’s machine sends an increasing number of requests to the device that is being targeted. This causes a persistent increase in network latency, which, if it is not appropriately addressed, might eventually result in the failure of the system.
-
Poor capacity usage of authorized traffic
In conclusion, a low throughput for legal traffic is another potential consequence of an ICMP flood attack. This is because the machine used by the attacker sends an overwhelming number of requests to the device that is being targeted, which causes it to become overwhelmed and unable to process any additional incoming traffic.
Is the ICMP Flood attack dangerous?
A target system may sustain considerable harm if it is subjected to an ICMP flood assault. It is possible for this to result in network congestion, the loss of packets, and increased delay, all of which have the potential to prevent routine data from reaching its destination.
In addition, by exploiting security flaws in the target’s system, an attacker may be able to obtain access to the target’s internal network and carry out further attacks.
Aside from that, the attacker may be able to carry out additional malicious operations, such as delivering enormous volumes of data that have not been requested or initiating distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against other computer systems.
How to prevent ICMP Flood attack
There are several measures that can be taken in order to prevent an ICMP flood attack.
Firewall and intrusion detection & prevention systems: Firewalls and Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) are two types of security software that can be utilized to identify and stop ICMP flood attacks. These systems are designed to monitor the traffic on a network and prohibit any suspicious behavior, such as unusually high packet rates or requests originating from a single source IP address.
Rate limiting: In order to protect against ICMP flood attacks, rate limiting is one of the most efficient preventative measures. In this method, you will determine the maximum number of requests or packets that can be transmitted to a target device in a certain amount of time by establishing a limit on that number. Any packets that are sent that are larger than this limit will be stopped by the firewall, and they will not be able to reach their intended location.
Source address verification: Verifying the source address of ICMP packets provides an additional layer of defense against these kinds of attacks. In this method, we check to see if data packets that are entering the network from outside the network actually come from the source address that they claim to be coming from. The firewall will block any packets that are unable to pass this verification, which will prevent those packets from ever reaching their intended location.
Network segmentation: Network segmentation is another line of defense against ICMP flood assaults that can be implemented. This is accomplished by segmenting the internal network into a number of smaller subnets and erecting firewalls between each of these subnets. This helps to ensure that an attacker is unable to access the entire system in the event that only one of the subnets is breached.
Protect your system from attacks from the ICMP Flood attack
An ICMP flood assault can do severe harm to a target system and is typically employed as a component of a more extensive and malicious attack.
You will be relieved to know that there are a number of preventative steps that you are able to take against attacks of this nature. These include rate restriction, the use of firewalls and intrusion detection and prevention systems, network segmentation, and source address verification. By putting these precautions into action, you can assist ensure that your system is secure and safeguard it from any prospective intruders.
Would you like to read more about ICMP flood attack-related articles? If so, we invite you to take a look at our other tech topics before you leave!
![]()