5G is the next generation of wireless network technology that will fuel innovation and transform the way we live, work, and play. It is the fifth generation of mobile networking. It is here to serve its purpose as it is getting more popular every day despite the ongoing pandemic and the recent rumors about the dangers of 5G (5G Vs. 4G). With the rise in work from home in 2020 and 2021, the 5G network coverage rollout may come faster than we think as more activities and businesses have now moved online. All three major service providers have now rolled out their nationwide networks. They are set to expand and improve their 5G mobile network rollout over the coming years. 5G has come, and it could surprisingly change the way technology is being used now.

5G networks can be built in different ways from multiple bands of wavelength spectrum: low-band, mid-band, and high-band. High-band millimeter-wave frequencies have greater bandwidth available to carry more data in dense urban areas but require cell sites to be nearby and have limited penetration in buildings. Mid-band balances speed and range, providing broader coverage than high-band. And it’s less impacted by buildings. Like our powerful 600MHz spectrum, low-band travels farther than other bands—over hundreds of square miles—and can pass through more obstacles, providing better coverage and a stronger signal both indoors and out.
Let’s find out if upgrading to 5G is really worth it and share what we need to know about the 5G mobile network to see if it’s crappy or worth the upgrade. Let’s begin by sharing the differences in the speed of 4G and 5G
5G Vs. 4G: Speed
We all know 5G will be faster than 4G, but let us share more specific information on the differences between the two mobile network speeds, though there isn’t a specific network speed we can expect. Instead, think of 5G as offering a speed range, and the actual speeds you get will depend on what wireless network you are connecting to, how busy it is, what device you are using, and a few other factors that need to be considered. The table below gives a rough idea of the average speed to maximum speeds of each generation of mobile network technology.
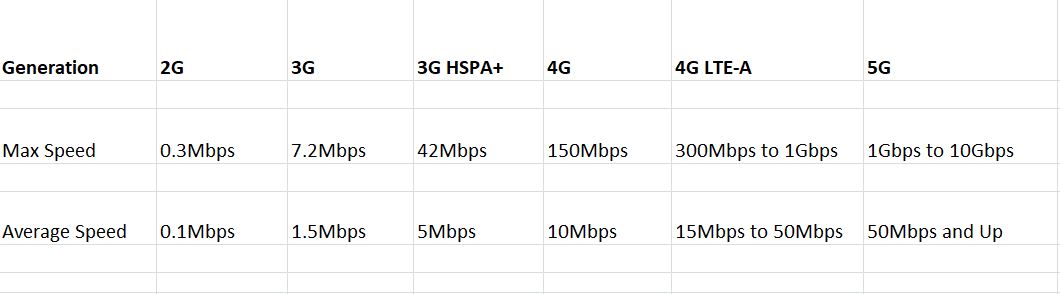
The average speed row above is more important than the max speed column because the peak speed here is theoretical. You will probably never really hit those download speeds.
More Details About Speed
The article topic is also complicated by the variety of different technologies used in each generation, geographical differences in coverage. And the fact that mobile technology continues to evolve and improve over time. For instance, 4G has improved significantly over its lifetime with the development of LTE (meaning Long-Term Evolution) and then LTE-A (meaning Long-Term Evolution Advanced). You can theoretically get up to 1Gbps with the latest 4G LTE-A developments in the range of what 5G is delivering. The average speeds you can get in the real world will inevitably be much lower.
Furthermore, to put that speed into some context, 1Gbps (gigabits per second) is 1,000Mbps (megabits per second). Confusingly, megabits are different from megabytes, and there are 8 megabits (Mb) in a megabyte (MB). So, 1Gbps translates to 125MB per second. An MP3 file might be 5MB, while a TV episode might be 350MB, and a Blu-ray movie will be 15GB (15,000MB) or more. So, if you actually have a 1Gbps connection, you could potentially download a Full HD Blu-ray quality movie in two minutes.
Meanwhile, 4G technology is still improving; what you get is, realistically, somewhere between 10Mbps and 50Mbps. If we look closely at Netflix’s recommendations for streaming speeds, it recommends 25Mbps for Ultra HD quality and only 5Mbps for HD movies. The purpose of 5G is to hit 50Mbps as an average minimum. However, the minimum is quite a bit lower right now, and the average is around 57Mbps now, according to Speedcheck. It’s always good to have faster speeds for streaming. But that’s not really the big attraction with 5G because 4G speeds are already pretty good. What 4G is not that great with is latency.
5G Vs. 4G: Latency
Latency means the time it takes for data from your device to be uploaded and reach its target. In other words, it measures the time it takes for data to go from source to destination in milliseconds (ms). It is essential for applications like gaming, where response time can impact the outcome. It could also prove vital for self-driving cars if data is being transmitted to the cloud, and quick decisions can trigger a reaction to break or avoid an obstacle in real-time.
With existing 4G networks, you are looking at an average latency of around 50ms. That could drop to 1ms with 5G technology. To give that some context, it takes at least 10ms for an image seen by the human eye to be processed by the brain. Low latency is bad for real-time reactions in machines or cars, and lower latency could make cloud gaming possible. Gamers could play through their phones on remote hardware, as services like Google’s Stadia and Blade’s Shadow suggest. A 1ms latency is what you can aspire to, as it’s possible in near-perfect scenarios. The average latency you can expect on 5G will likely be around 10ms. Reduced latency could prove to be the real driver for 5G deployment and adoption, but there are many challenges ahead.
5G Vs. 4G: Coverage
It has taken years for 4G networks to spread across the world, and there are still plenty of rural areas relying on 3G networks. Even where there is 4G coverage, the speeds vary quite widely. We expect the full rollout of 5G networks to take a while; however, all three major carriers have made some pretty big advancements in 5G coverage over the past few months. All three major carriers now offer “nationwide” networks based on the Sub-6 spectrum and are set to build out those networks with other spectrum and wide coverage over the next year for 5G vs. 4G.
For the uninitiated, 5G is built with a full array of different radio frequencies. Sub-6 refers to frequencies under 6GHz, and these waves can generally travel long distances but can’t support ultra-high download speeds. On the other end of the 5G spectrum is mmWave, which offers a huge advantage in download speed but can’t travel far or penetrate obstacles in 5G Vs. 4G.
Initially, Verizon employed mmWave for its 5G network, and as such, you could only really connect to Verizon 5G in some areas of some cities. Thankfully, the company now uses Sub-6 for its nationwide mobile network, something T-Mobile did from the beginning.
Differences Between 5G and 4G
To take advantage of 5G mobile network connectivity, we do not just need carriers to put network equipment in place. We also need to buy a 5G device, like the Motorola One 5G Ace. If you’ve picked up one of the latest 5G smartphones, you may be able to enjoy 5G speeds, depending on where you live. But if your mobile phone is older, you will need to consider upgrading if you want these faster speeds. The first batch of 5G smartphones is here, and there are already some great choices available, like the Samsung Galaxy Note 20 Ultra 5G or the OnePlus 8 Pro. It’s also worth noting that 5G is likely to be much more demanding in terms of power, and so battery life, which is already an issue for many, could be about to get worse. 5G vs. 4G
More Differences Between 5G and 4G
The fact is that many of us still rely on 3G when a 4G network isn’t available, and that’s exactly what will happen with 5G. The idea that 5G is a direct replacement for 4G is erroneous. In fact, it’s a complementary technology. With the two workings in tandem, you should be able to get good or at least decent speeds on your mobile device wherever you are.
It’s also important to remember that carriers continue to upgrade 4G networks. And that both download speeds and latency can be improved further. Even though carriers are spending more time and resources on 5G wireless technology, 4G networks will likely continue to improve, resulting in faster speed across the board. The fifth-generation (5G) of network technology can benefit everything from entertainment and gaming to education and public safety. Over time, 5G is expected to deliver faster download speeds, real-time responses, and enhanced connectivity, giving businesses and consumers the potential to experience new, innovative technologies in 5G Vs. 4G.
Would you like to read more about 5G Vs 4G-related articles? If so, we invite you to take a look at our other tech topics before you leave!
![]()













